Buyer's Guide
Embark on a journey through our comprehensive buyer's guide, where you'll delve into the enchanting realm of gemstones, diamonds, birthstones, and anniversary stones. Whether you seek timeless elegance, astrological significance, or symbolic gestures, our curated insights and alternatives ensure you find the perfect stone for every occasion.The Four Cs of Diamonds
diamonds are so valuable, it’s essential to have a universal grading system for comparing their quality. In the 1940s and ’50s, GIA developed the 4Cs and the GIA International Diamond Grading System™ to objectively compare and evaluate diamonds. Read more here.

Carat
Diamonds and other gemstones are weighed in metric carats: one carat is equal to 0.2 grams, about the same weight as a paperclip. (Don’t confuse carat with karat, as in “18K gold,” which refers to gold purity.) Just as a dollar is divided into 100 pennies, a carat is divided into 100 points. For example, a 50-point diamond weighs 0.50 carats. But two diamonds of equal weight can have very different values depending on the other members of the Four C’s: clarity, color and cut. The majority of diamonds used in fine jewelry weigh one carat or less.


Color
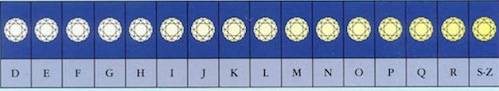
Diamond color is all about what you can’t see. Diamonds are valued by how closely they approach colorlessness – the less color, the higher their value. (The exception to this is fancy-color diamonds, such as pinks and blues, which lie outside this color range.) Most diamonds found in jewelry stores run from colorless to near-colorless, with slight hints of yellow or brown.
GIA’s color-grading scale for diamonds is the industry standard. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues with increasing presence of color to the letter Z, or near-colorless.

Clarity
Because diamonds formed deep within the earth, under extreme heat and pressure, they often contain unique birthmarks, either internal (inclusions) or external (blemishes). Diamond clarity refers to the absence of these inclusions and blemishes. Diamonds without these birthmarks are rare, and rarity affects a diamond’s value. Using the GIA International Diamond Grading System™, diamonds are assigned a clarity grade that ranges from flawless (FL) to diamonds with obvious inclusions (I3).
Every diamond is unique. None is absolutely perfect under 10× magnification, though some come close. Known as Flawless diamonds, these are exceptionally rare. Most jewelers have never even seen one.


Cut
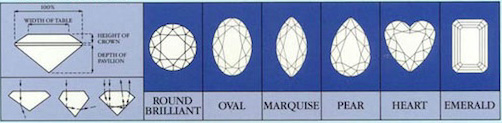
Cut is the factor that fuels a diamond’s fire, sparkle and brilliance. The traditional 58 facets in a round brilliant diamond, each precisely cut and defined, are as small as two millimeters in diameter. But without this precision, a diamond wouldn’t be nearly as beautiful. The allure of a particular diamond depends more on cut than anything else.
An understanding of diamond cut begins with the shape of a diamond. The standard round brilliant is the shape used in most diamond jewelry. All others are known as fancy shapes. Traditional fancy shapes include the marquise, pear, oval and emerald cuts. Hearts, cushions, triangles and a variety of others are also gaining popularity in diamond jewelry.
How To Buy Gemstones
Prized for centuries for their beauty, and often used as currency, gemstones hold ageless appeal. Modern treating techniques enhance their look and improve their durability. Whatever your favorites--rubies, sapphires, emeralds or others--find a good jeweler to buy from. Read more here.
-
Work with a jeweler you trust.
Work with a jeweler whose character you trust. Since virtually all gemstones are treated, the opportunity for deception is great-- you want to be dealing with someone you can depend on. If something about the experience is off-putting, leave.
-
Learn about lab-created and treated stones
Learn about lab-created and treated stones. Ask jewelers if a naturally mined stone has been treated--heated, bleached, coated or dyed to improve the look or durability. Some treatments can weaken a stone and lower its price.
-
Beware imitations!
Keep your eyes open for imitations, generally made of glass or plastic. Jewelers will tell you what's what.
-
Apply 'The Four Cs'
Apply the four Cs to buying gemstones just as you would to purchasing diamonds . Gemstones, however, don't carry letter grades for guidance; a trustworthy jeweler will show you how to be discerning.
-
Shop Around
Numerous companies operate in the field of colored gems, so prices fluctuate far more widely than those of diamonds, and it pays to watch them over time. A one-carat ruby, for instance, can vary enormously in cost--and may be just as expensive as a diamond. And gems over three carats in size leap up in price because they are rare. Color--shade and saturation (whether the color is dull or intense)--also greatly affects price. Clarity is also important (the gem should have few flaws or inclusions), as is a perfect, light-reflecting faceted cut.
-
Check Return and Refund Policy
Check the store's return and refund policy before finalizing your purchase.
-
Paperwork!
Make sure your receipt details all the stone's specifications including its weight and size. Ask for a grading report, and check that the receipt specifies whether the stone is a natural gem, lab-created or treated stone.
Traditional Birthstones

Zodiac stone and other commonly associated birth stones.
Unlock celestial connections with zodiac stones, aligning with astrological signs for meaningful adornment. From fiery rubies for passionate Leos to serene aquamarines for balanced Libras, these stones harmonize with individual energies.
- Aquarius (Jan 21-Feb 18)
- Pisces (Feb 19-Mar 20)
- Aries (Mar 21-Apr 20)
- Taurus (Apr 21-May 21)
- Gemini (May 22-Jun 21)
- Cancer (Jun 22-Jul 22)
- Leo (Jul 23-Aug 23)
- Virgo (Aug 24-Sep 22)
- Libra (Sep 23-Oct 23)
- Scorpio (Oct 24-Nov 22)
- Sagittarius (Nov 23-Dec 21)
- Capricorn (Dec 22-Jan 20)
- Garnet, Amethyst, Moss Agate, Opal, Sugilite
- Amethyst, Aquamarine, Bloodstone, Jade, Rock Crystal, Sapphire
- Bloodstone, Diamond
- Sapphire, Amber, Coral, Emerald, Rose Quartz, Turquoise
- Agate, Chrysoprase, Citrine, Moonstone, Pearl, White Sapphire
- Emerald, Moonstone, Pearl, Ruby
- Onyx, Carnelian, Peridot, Sardonyx, Golden Topaz, Tourmaline
- Carnelian, Jade, Jasper, Moss Agate, Blue Sapphire
- Peridot, Lapis Lazuli, Opal, Peridot
- Beryl, Apache Tear, Aquamarine, Coral, Obsidian, Topaz
- Topaz, Amethyst, Ruby, Sapphire, Turquoise
- Ruby, Agate, Garnet, Black Onyx
Wedding Anniversary Stones
Celebrate milestones with anniversary stones. Symbolizing each year, from traditional diamonds to unique peridots, they capture love's evolution. Alternate stones are listed in parentheses.
- 1st: Gold (Peridot)
- 2nd: Garnet
- 3rd: Pearl (Jade)
- 4th: Blue Topaz (Blue Zircon)
- 5th: Sapphire (Pink Tourmaline)
- 6th: Amethyst (Turquoise)
- 7th: Onyx (Yellow Sapphire, Golden Beryl)
- 8th: Tourmaline (Tanzanite)
- 9th: Lapis Lazuli (Amethyst, Green Spinel)
- 10th: Diamond (Blue Sapphire)
- 11th: Turquoise (Citrine, Yellow Zircon)
- 12th: Jade (Opal)
- 13th: Citrine (Moonstone, Hawk's Eye)
- 14th: Opal (Agate, Bloodstone)
- 15th: Ruby (Rhodolite Garnet, Alexandrite)
- 16th: Peridot (Red Spinel)
- 17th: Wristwatch (Carnelian)
- 18th: Cat's Eye / Chrysoberyl (Aquamarine)
- 19th: Aquamarine (Almandine Garnet)
- 20th: Emerald (Yellow or Golden Diamond)
- 21st: Iolite
- 22nd: Spinel
- 23rd: Imperial Topaz
- 24th: Tanzanite
- 25th: Silver (Tsavorite, Green Garnet)
- 30th: Pearl
- 35th: Emerald
- 40th: Ruby
- 45th: Sapphire (Cat's Eye)
- 50th: Golden (Imperial / Golden Topaz)
- 55th: Alexandrite
- 60th: Diamond (Star Ruby)
- 65th: Blue Spinel
- 70th: Sapphire (Smoky Quartz)
- 75th: Diamond
- 80th: Ruby
